In this chapter, we will cover the following topics:
- Data security
- Data privacy
- Data security and privacy features in a CDP
- Cookie-less tracking and its impact
- Future of data security and privacy
Let us understand what data security is. Data security refers to the protection of data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. It involves implementing measures and safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data. Data security aims to prevent unauthorized individuals or entities from gaining access to sensitive information and to mitigate the risks associated with data breaches, cyberattacks, or accidental data loss.
It’s a concept that encompasses every aspect of information security, from the physical security of hardware and storage devices to administrative and access controls, as well as the logical security of software applications.
Why is data security so crucial?
To understand the cost implication of data security, here is a finding: “According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average data breach costs rose from $3.86 million to $4.24 million in 2021—the highest average total cost in the 17-year history of their report.”
The cost of a data breach per country is shown in Figure 7.1:
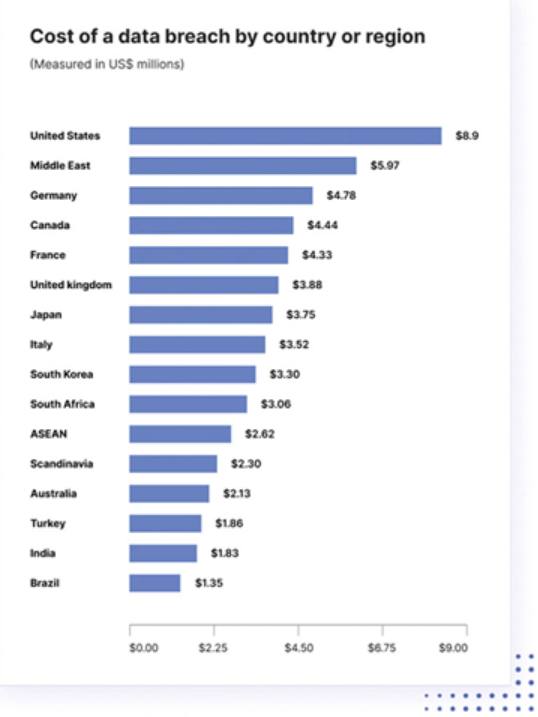
Figure 7.1: Cost of data breach in different countries (source-https://www.imperva.com/learn/data-security/data-security/)
A data breach is not only bad financially as it can lead to fines and penalties, but it also damages the years of reputation a company has gathered. A company data breach will destroy the trust and confidence of its customers and clients.
Data security is crucial due to the following factors:
- Protecting Confidentiality: Data security ensures the confidentiality of sensitive information.
- Safeguarding Integrity: Data integrity refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data.
- Ensuring Availability: Data security measures also ensure the availability of data when needed.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries and jurisdictions have specific data protection regulations and standards that organizations must comply with. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties and legal consequences.
- Maintaining Customer Trust: In an era where data breaches and privacy incidents are increasingly common, maintaining customer trust is paramount.

