After connecting the data sources, next we ingest the data into Data Cloud. Before we can move to data modeling, it is important to understand how the data is ingested in the Data Cloud. Creating your data model can be a challenging task. It requires a thorough understanding of the data collection methods, the current data structure, and the relationships between different data sources. Additionally, it entails consolidating all this data into a comprehensive and useful customer view. Salesforce Data Cloud provides you with the necessary tools to accomplish this goal by enabling the creation of a unified customer view, empowering you to effectively engage with your customers.
There is a two-phased approach to bringing the data, as follows:
- Data ingestion: Ensure that all fields from a data set are brought in without any alterations. This way, you will always have the option to revert to the original data format if needed, especially in case of errors or changes in business requirements during the setup process. Additionally, you can expand the data set by creating extra formula fields to tidy up nomenclature or perform calculations on a row-by-row basis. Each data set will be represented by a data stream in Data Cloud.
- Data modeling: Map the data streams to the data model to create a harmonized view across sources.
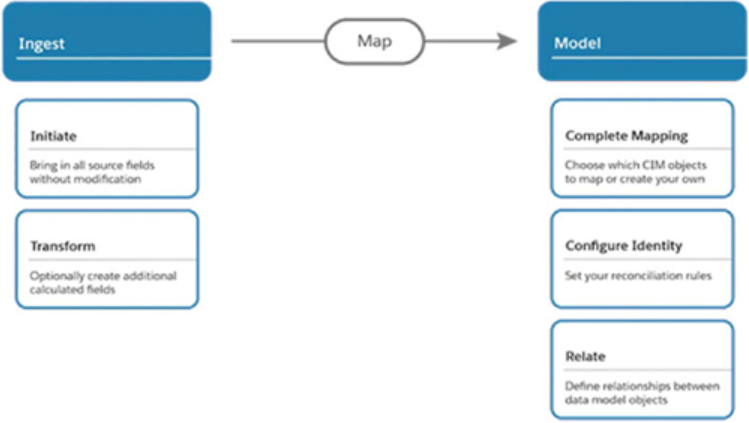
Figure 6.11: Steps to bring in data in Data Cloud (Source: https://trailhead.salesforce.com/content/learn/modules/customer-360-audiences-data-ingestion-and-modeling/prepare-to-build-your-data-model?trail_id=explore-customer-360-audiences)
Let us understand how the Data Cloud data model works before we proceed with the steps for data modeling.
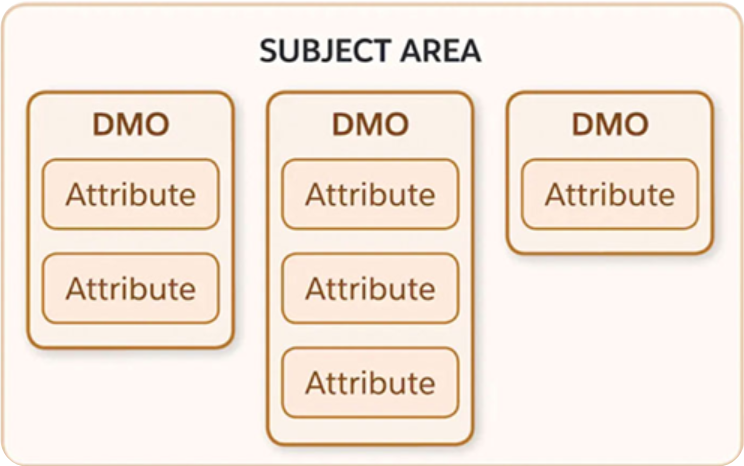
Figure 6.12: Salesforce Data Cloud Data Model (Source: https://trailhead.salesforce.com/content/learn/modules/customer-360-audiences-basics/get-to-know-the-cloud-information-model#:~:text=For%20marketers%2C%20the%20Customer%20360%20Data%20Model%20is,or%20tracking%20customer%20loyalty%20are%20called%20data%20bundles)
Subject Area
A subject area is a business concept or term used to group similar data objects to aid in data modeling, for example, sales orders, loyalty, or engagement data. Each subject area contains one or more data model objects.
Data Stream
A data source brought into Data Cloud, for example, a Marketing Cloud customer data extension. These data streams can be based on batched data or real-time data streams.
Data Model Object (DMO)
A data model object (DMO) is a collection of data, consisting of attributes, which is formed from data streams, insights, and other data sources. These DMOs can be categorized as standard or custom, depending on the specific requirements of the business. Standard DMOs typically include common entities such as sales orders, party identification, email engagement, and more. Custom DMOs, on the other hand, are tailored to address the unique needs of the organization.
Attribute
An attribute, sometimes referred to as a field, is a particular piece of information present in a DMO, such as a customer’s first name. This is comparable to a Marketing Cloud data extension field.
Foreign Key
A foreign key is a common link found between data sources that build data relationships, for example, a customer ID number.

